Overview
 Skin is the body's largest organ. Skin plays an important role in protecting the body from environmental factors, helping the body retain moisture and regulating temperature. Skin is the body's largest organ. Skin plays an important role in protecting the body from environmental factors, helping the body retain moisture and regulating temperature.
The skins epidermis (outer layer) protects the skin's inner structure, known as the dermis. It is a protective coating to the skin and is made up of cells which are continuously dying and being replaced by new living cells. In young skin, cells are renewing themselves at a rapid rate. These cells migrate upward to the epidermis replacing dead, dry cells. As we age, the process of cell turnover slows down and takes longer to produce new cells. This slowdown results in a loss of new, fresh skin.
In addition to the key biological role skin plays, the skins appearance is paramount to a woman's feeling of well-being and physical attractiveness. How a woman's skin looks is directly linked to her overall health and wellness. When the body is fatigued, poorly nourished or stressed, the skin shows it.
Free Radicals
Chemically, free radicals are highly reactive substances that have a single unpaired electron in their outer most orbits. They are generally unstable and try to become stable, either by accepting or donating an electron. When free radicals react with stable molecules, there is generation of more free radicals. This characteristic enables the free radicals to participate in auto catalytic chain reactions, propagating more free radicals and resulting in cell damage.
In lay terms, free radicals are substances found throughout the body that, under certain conditions, can be highly toxic, cause cell damage and premature aging. Free radicals are by-products of many environmental factors such as UV radiation, tobacco smoke, air pollution and stress. When free radicals are generated inside the body, they can damage healthy skin cells. The best defense against free radicals is antioxidants.
The body produces antioxidants, but stress, the aging process and other influences result in decreased production.
Photo Aging
Dermatologists use this term when referring to certain types of sun-induced skin damage. Photo aging is a process that starts in youth, although the more obvious skin changes, such as wrinkles, freckles, leathery texture and loss of elasticity, may not become evident for decades. Using a high-SPF sunscreen (SPF 15 or above) on a regular basis can help protect the skin from further damage. There is also evidence to suggest that the skin has the ability to heal itself if protected, thereby reversing some of the signs of photo aging.
Unfortunately, the suntanned look, which seems to be the badge of glowing health, is in fact the opposite - and it does not matter if you acquired the tan under the sun or at a tanning salon - the UV rays are harmful to your skin. Not only does sunlight cause premature aging, it is the leading factor for skin cancer including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
 |
 |
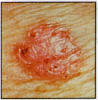 |
| Melanoma |
Basal Cell |
Squamous Cell |
Although 80% of Americans are aware of the damage that sun exposure can cause, less than half take steps to protect themselves. During sun exposure, free-radicals are formed. Free radicals are unstable oxygen molecules that scavenge other molecules and in so doing set off a chain reaction which leads to cell deterioration. As we age, we have a degeneration of collagen, however, the sunlight speeds up this breakdown process
 and also causes the build up of abnormal elastin. UV radiation also causes the walls of blood vessels to lose some of their integrity, and in doing so can cause bruising in the skin. Indirect sunlight is also damaging to your skin, and indirect sunlight / reflected sunlight can still retain more than a third of its UV rays.
and also causes the build up of abnormal elastin. UV radiation also causes the walls of blood vessels to lose some of their integrity, and in doing so can cause bruising in the skin. Indirect sunlight is also damaging to your skin, and indirect sunlight / reflected sunlight can still retain more than a third of its UV rays.
How to Prevent Photo Aging
Steps to preventing the damaging effects of photo aging:
| ● |
avoid being outdoors when the sun is most intense, from 10:00am – 4:00pm |
 |
|
|
| ● |
wear a hat, long sleeves, and close knit clothing while in the sun |
|
|
 |
| ● |
use a sunscreen with a SPF of 15 or higher and choose a brand that protects against both UVA and UVB radiation (the label will give you this information). At least ½ hour prior to going out, apply sunscreen to every part of your body that is exposed, including your ears, lips, nose, neck and hands. Don't forget the top of your head if your hair is thinning or scalp is exposed. |
|
|
|
|
|
| ● |
protect your eyes and the delicate skin around your eyes. Because sun exposure can cause eye disorders later in life, you should invest in a pair of good quality sunglasses. It is best to consult an optometrist about the best type of sunglasses, but the general consensus is that polarized lenses with a gray tint, brown or dark green are the best. If the lenses are too dark, pupils can dilate (widen) too much, and could allow potentially harmful rays to reach the retina in the eye. The delicate skin around the eyes is often forgotten when it comes to sun protection. While sunglasses offer partial protection, sunscreen should also be applied to this area, being careful to avoid the eyes.
Follow-up with a quality skin care product made specifically for the skin around the eyes such as OcuDerma®, ocular skin therapy.
|


|
Diet and Skin Care
Week by week, magazine articles carry dozens of suggestions as to how we could make our skin healthier. As we have seen, healthy skin is the consequence of a well-hydrated and intact epidermis, together with avoidance of sun damage and a balanced diet.
Most Americans do not consume the recommended intake of five servings of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains daily. This can lead to inadequate levels of important vitamins and minerals that women need for optimal health.
Supplementing Your Diet
Taking a daily multivitamin/multimineral supplement has long been recognized as an important part of helping to maintain good health. More recently, the scientific community and researches have begun to direct their efforts to investigate the relationship between nutrition and skin health. Vitamins and minerals are used routinely in topical skin treatment for their beneficial effects on the skin's surface and as antioxidants. Now, greater emphasis has been placed on obtaining vitamins and minerals from the inside (through good nutrition) to support good skin health in addition to the use of creams and lotions on the outside.
 Taking a daily dietary supplement, such as
DERMAVITE® for maintaining healthy skin is a new paradigm. Over the past few years, studies have shown that specific vitamins and minerals, when taken orally, can help maintain healthy
skin appearance, beauty, and overall well being. Many skincare experts believe that a daily nutritional supplement for healthy
skin should be a part of a lifestyle that includes a nutritious, balanced diet, regular exercise and plenty of sleep.
Taking a daily dietary supplement, such as
DERMAVITE® for maintaining healthy skin is a new paradigm. Over the past few years, studies have shown that specific vitamins and minerals, when taken orally, can help maintain healthy
skin appearance, beauty, and overall well being. Many skincare experts believe that a daily nutritional supplement for healthy
skin should be a part of a lifestyle that includes a nutritious, balanced diet, regular exercise and plenty of sleep.
Dermal-Specific Nutrients
When choosing a nutritional supplement for healthy skin, consider these nutrients:
|

